INTRODUCTION-
Living organisms have a limited
lifespan. Unless they are not going to form new organism, they will finish.
Their continuity of life will be lost. So, fertile organisms form new organism
of same kind either by self or by the help of other individual of same species.
The process of formation of similar types of organisms by existing organism is
called reproduction.
There are two types of reproductions-
(a) Asexual Reproduction – New organism is formed by single parent. It
is common in plants
and animals.
(b) Sexual Reproduction- New organism is formed by two parents. It is
common in plants
and animals.
A. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS - New
organism is formed by a single parent. It occurs by following methods-
1. Vegetative Propagation- The
vegetative parts of plant is used to grow the new organism. e. g.- Roots in
case of Sweet Potato and Mint, Stem in case of Strawberry and Chrysanthemum,
Modified stem in case of Potato tubers, Leaves in case of Bryophyllum and
African violet is used to develop new organism.
Vegetative Propagation also occurs by artificial methods like- Cutting, Grafting, Layering and Tissue culture. It is very useful for fruit yielding plants.
2. Budding- Bud is an asexual
reproductive structure. This is an outgrowth of mother body in which a nucleus
is found. The bud grows to form the new organism. e.g. – Yeast (A Fungus)
3. Fragmentation- Fragments are
small asexual reproductive structures formed by fragmentation of mother body. Each
fragment grows into a new organism. e. g.- Spirogyra
4. Spore Formation- Spores are
small asexual reproductive structures that germinate to form new organism.
Spores are formed in large number. They float in air and on finding suitable
surface for germination, they form new organisms. The germinating surface must
contain organic matter and water. e. g.- Ferns (Pteridophytes) and Fungi like
Rhizopus, Mucor, Penicillium, Agaricus (Mushroom) etc.
B. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS- The
reproduction in which two parents, one male and one female are required to form
the new organism is called as sexual reproduction.
Uni-sexual and Bisexual Flowers- Those incomplete
flowers which have either pistil or stamen are called uni-sexual flowers. e.
g.-Papaya, Maize, Cucumber etc.
Those flowers which have both pistil as well as stamen are called as bisexual
flowers. e. g.- Rose, china-rose, mustard, marigold, lotus etc.
Pollination- The transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma is
called pollination. There are two types of pollinations-
A. Self fertilization
B. Cross fertilization
When transfers of pollen grains occur from anther to the stigma of same
flower, it is called as self fertilization. When transfers of pollen grains occur from
anther to the stigma of different flower, it is called as cross fertilization.
On stigma, pollen grains germinate to form pollen tube in which male
gametes are found. The pollen tube moves below inside the ovary for
fertilization.
Fertilization- The fusion of male gamete with female gamete to form zygote
is called fertilization. As a result of fertilization, single celled zygote is
formed.
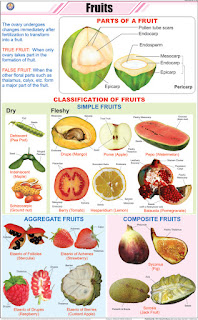
Formation of Fruits and Seeds- As a result of fertilization some
post-fertilization changes starts. The ovary changes into fruit and ovules
change into seeds. So, fruit is ripened ovary.
Seed- The seed develops from the
fertilized ovules. They have an outer protective covering called seed coat. The
Seed has either one cotyledon or two cotyledons. Cotyledons are nutritive cells
that give food to developing radical and plumule.
Seed Germination- The seeds
can remain in dormant stage for many months to many years. On finding suitable
conditions, the seed germinate to form radicle and plumule. The small embryo
develops into radicle and plumule. The root system develops from radicle and
shoot system develops from plumule.
Seed Dispersal- The method of going
of seed from one place to other by an agent is called seed dispersal. The
agents to seed dispersal can be- air, wind, water, animals including humans,
bats, explosion etc.
Some seeds have hairy structures and
wings so they are carried away by wind to other place.





















No comments:
Post a Comment